Serial Input Paralel Output Sipo
CD4099B 8-bit addressable latch is a serial-input, parallel-output storage register that can perform a variety of functions. Data are inputted to a particular bit in.
5.7.1 Parallel In/Parallel Out (PIPO) Register An electronic register is a form of memory that uses a series of flip-flops to store the individual bits of a, such as a byte (8 bits) of data. The length of the stored binary word depends on the number of flip-flops that make up the register. A simple 4-bit register is illustrated in Fig. 5.7.1 and consists of four, sharing a common input, providing synchronous operation ensuring all bits are stored at exactly the same time.
The binary word to be stored is applied to the four D inputs and is remembered by the flip-flops at the rising edge of the next clock (CK) pulse.  The stored data can then be read from the Q outputs at any time, as long as power is maintained, or until a change of data on the D inputs is stored by a further clock pulse, which overwrites the previous data. Different types of register are generally classified by the method of storage and readout used; this basic form of register is therefore classified as a ‘Parallel In/Parallel Out’ (PIPO) register. Shift Registers.
The stored data can then be read from the Q outputs at any time, as long as power is maintained, or until a change of data on the D inputs is stored by a further clock pulse, which overwrites the previous data. Different types of register are generally classified by the method of storage and readout used; this basic form of register is therefore classified as a ‘Parallel In/Parallel Out’ (PIPO) register. Shift Registers.
Shift registers have a similar structure to the PIPO register but have the added ability to shift the stored binary word left or right, one bit at a time. This makes them extremely useful for many applications. They are used in handling serial data and converting it to parallel form or back again to serial form, and therefore are an essential component in communication systems. Shift registers are also essential in arithmetic circuits where binary numbers may be shifted right (and so divided by two), or left (multiplied by two) as part of a calculation.
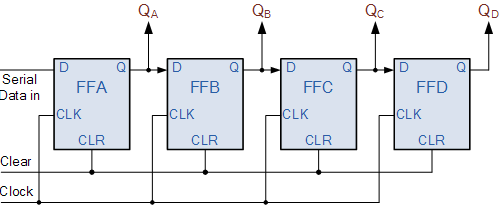
Shift registers can be used to delay the passage of data at a particular point in a circuit. As the data is shifted one bit at a time from input to output, the amount of delay will depend on the number of flip-flops in the register and the frequency of the clock pulses driving the shift register. Because a number of serial bits of data are stored as they enter the input, and are then recovered from the output at some later time, this action can also be described as a serial memory, or as a digital delay line. 5.7.2 Serial In/Serial Out (SISO) Shift Register The simple storage register shown in Fig. 5.7.1 can be modified to a shift register by connecting the output of one flip-flop into the input of the next, as shown in Fig. The basis of shift register circuits is the D-type flip-flop, but the or the may also be converted to D-types by the inclusion of an inverter between S and R or between J and K. In all cases the clock input is in synchronous mode.
The serial input of the shift register in Fig. 5.7.2 is the D input of the first flip-flop, and the serial output is the Q output of the last flip-flop in the chain. The logic state at the serial input appears at the output, a number of clock pulses (equal to the number of flip flops) later. 5.7.3 Timing Diagram and State Table for SISO Operation Modes of Shift Register Operation. SISO A State Table and Timing Diagram illustrating the operation of Fig.5.7.2 is shown in Fig.
5.7.3 where the timing diagram shows the time relationship between the CK pulses and changes at the Q outputs of the circuit. It can be seen that if the serial input goes from 0 to 1 just before CK pulse 1, the Q output of flip-flop FF0 will go high at the rising edge of CK pulse 1. At the next clock pulse rising edge, the logic 1 will be transferred to FF1 and so on until it reaches FF3, and the serial output. The same action can also be illustrated by a State Table, which, rather than showing timing data, shows the states of the four Q outputs after each clock pulse. After each CK pulse one more flip-flop output is set to 1 until, after 4 pulses, column 4 shows that all Q outputs, including the serial output, are at logic 1. Game sex 3d crack mien phi. This form of operation is called ‘serial in/serial out’ or SISO.
5.7.5 Multiple Mode (SISO, SIPO, PISO, PIPO) Shift Register If use is also made of the Q output, and the additional preset ( PR) and clear ( CLR) inputs available on many flip-flops, the shift register could be made more versatile still. 5.7.5 shows a shift register modified to enable it to be loaded with a 4-bit parallel number, which may then be shifted right to appear at the serial output one bit at a time. As the ‘Parallel In/Serial Out’ or PISO register also has a serial input, it can also be used as a SISO register, and if extra outputs from each Q output were also included, the register would also have Serial In/Parallel Out (SIPO) operation. Loading Parallel Data If the LOAD input is taken to logic 0, the LOAD control line connected to the four pairs of NAND gates associated with the four flip-flops will be at logic 1, and all four pairs of NAND gates will be enabled. Therefore a logic 1 appearing on any of the D inputs will be inverted by the NOT gate connected to the D input, making the inputs to the left hand NAND gate of the relevant pair of gates, logic 1 and logic 0.